Is Blue Light Safe
In this week’s blog we are going to answer the question, is blue light safe? We are also going to give you some easy solutions to limit your exposure of blue light.
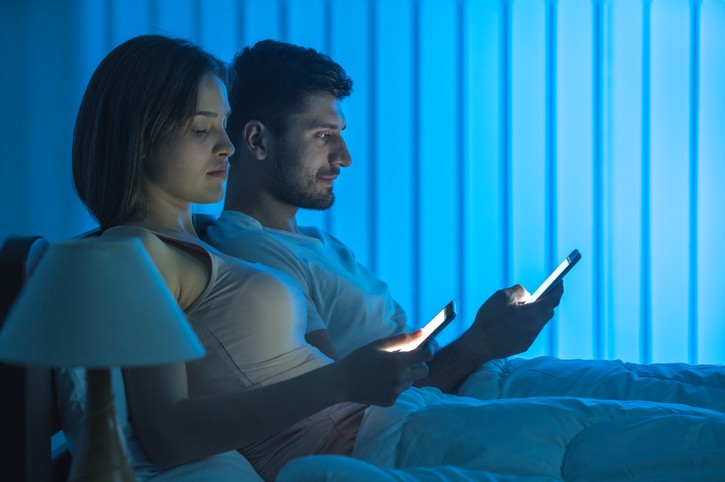
In todays ever busy, fast paced burn the candles at both ends way of life, the majority of people are no longer living by the rise and fall of the sun. Modern technology and conveniences allow for productivity or just plain business to happen day and night. With the introduction of artificial light, cellular phones, desktop and laptop computers, tablets and televisions our mind and body can be easily over stimulated. We will discuss what are the concerns with too much blue light, are we adapting to these progressive changes in a positive way, and finally what are the health implications of the “blue light” effects of all these technologies.
What is blue light?
Sunlight, white light or visible light contains the color spectrum of red, orange, yellow, green, blue and violet. As a color moves along the spectrum from red to violet the wavelength of the particles in that color become smaller. Inversely the energy produced by the wavelength of color becomes larger. So blue/violet light is a high energy light making up approximately one third of the visible light to humans.
Natural vs Artificial Light?
Although sunlight is usually the main source of blue light, our busy indoor lives has limited outdoor exposure to “natural light”. We have become more exposed to the artificial “blue light” through florescent, LED, flat screen televisions, computer screens, tablets, smart phones and other digital devices.
Why is blue light more of a concern than other colors on the spectrum?
The National Sleep Foundation studies determined the following related to blue light and its effects on human physiology- “Blue light…has a short wavelength that affects levels of melatonin more than other wavelengths.”
The increase in blue light exposure, especially in the evening hours, alters timing of the pineal gland to release melatonin. These alterations result in longer times to fall asleep, less REM sleep and waking up tired even with eight hours of sleep.
Changes to the sleep cycle, or circadian rhythms is directly affected by individual exposure to blue light. Increased blue light exposure stimulates the pineal gland to stop melatonin production and facilitates wakefulness. This makes blue light exposure vital during the day because it helps keep us awake. At night, around 9 pm, normal pineal gland function starts an increase production of melatonin to help us fall asleep
If nighttime activities have an increased exposure to blue light through the “screen time” and artificial lighting, then significant negative effects can result.
Researchers, in a 2011 Journal of Applied Medicine study, found two hours of blue light exposure in the evening suppressed melatonin enough to result in sleep disturbances.
Sleep disturbance is not the only effect of too much blue light exposure. Melatonin has antioxidant properties for our body’s cells, especially the powerhouse of the cell, the mitochondria. The suppression of melatonin also limits the role melatonin plays in reducing potential risk of cancer and metabolic disorders.
Over exposure of blue light has shown to kill photoreceptor cells of the eye by stimulating increased production or retinal. Since retinal is found throughout the body, further studies may determine a broader toxicity of retinal to the body may be occurring.
Blue light overexposure has some well researched negative effects on human anatomy and physiology. However, appropriate exposure during normal sunlight hours has shown to help memory and cognitive function, boost alertness and elevate mood. Daytime exposure also helps maintain healthy circadian/sleep rhythms.
Blue Light Recommendations
General recommendations are to limit “screen time” once the day turns to night. Over exposure to blue light can also be reduced by the use of “blue blocking” glasses, screens for computer monitors and specific applications or settings on smart phones.
As a support to the body’s cellular function, especially photocells, alpha-tocopherol, derived from vitamin E, has shown to stop cell death when cells were exposed to retinal and blue light. Some foods that contain high amounts of vitamin E are sunflower seeds, almonds, spinach, avocado and asparagus.
Maintain the health of your eyes and nervous system by limiting your artificial “blue light” exposure, especially in the night hours, balancing a whole food diet, minimizing stress with exercise and have a spinal check-up with your chiropractor.
We started this blog with asking the question, is blue light safe. And after reviewing the research it is our opinion that ones ability to limit blue light is going to have positive effects on your health and immune system.
Reed Chiropractic
Call or Click to schedule a wellness exam and consultation with one of our doctors.